 Controlling Access in Loftware Enterprise SP
Controlling Access in Loftware Enterprise SP
Loftware Enterprise™ SP uses a combination of role-based access control and object-based access control to provide security. Administrators can specify what objects a user has access to and what actions a user can perform on a given type of object.
Important! For a user to be able to perform an action on an object, the user must have both role-based permission to perform the action on that type of object and object-based permission to perform that action on the object.
Authenticating Users
Loftware Enterprise SP has the concept of local and domain users. Local users are assigned a password by the administrator within the Loftware Enterprise SP system. Domain users are configured in Loftware Enterprise SP, but their passwords are stored in an LDAP or Federated Single Sign-On system.
If you use an LDAP, Azure, or Single Sign-On system, Loftware Enterprise SP can use that system to authenticate the user. You can also configure auto-provisioning to automatically create and update users and group assignments. For more information, see Configuring Authentication.
Configuring Access
At a basic level you perform the following tasks when configuring security in Loftware Enterprise SP.
- Create a folder structure that makes sense for your organization. When creating each folder, decide whether you want to have for objects in that folder.
- Review the built-in roles and the permissions for role-based access control that they provide. If necessary, create additional roles.
- Create groups.
- Create users.
- Assign roles to groups or users.
- Assign group membership to users.
- Configure permissions for folders. Ensure that the objects on which a role must act allow the action to be performed. For example, this can include allowing access to a folder, label template, device, data service, integration, or process.
Restrictive versus Permissive Security
In a restrictive security configuration, you block access to most or all objects (also called entities) by default and then selectively grant access to specific users or groups. This approach is also known as whitelisting. By default Loftware Enterprise SP has restrictive security. All permissions except List permission for Folders are denied.
In a permissive security configuration, you allow access to most or all objects by default and then selectively block access by specific users or groups. This approach is also known as blacklisting.
Access Concepts in Loftware Enterprise SP
Loftware Enterprise SP provides a powerful and flexible security model for access control. Depending on your background, this security model may include dimensions that are new to you.
 A permission can be granted or denied
A permission can be granted or denied
A permission is the potential for a user to be able to perform an action. A permission can be granted or denied. Permissions can be granted or denied directly, or they can be inherited.
 Permissions are specific to object type
Permissions are specific to object type
In Loftware Enterprise SP, permissions are specific to the type of object. For example, instead of a generic Create permission, there is a separate Create permission for each type of object, such as Create permission for Folders, Create permission for Users, Create permission for Documents, and Create permission for Data Services. A user may be granted Create permission for Documents, but denied Create permission for Integrations.
 Both object access permission and role-based permission are required
Both object access permission and role-based permission are required
There are two categories of permissions in Loftware Enterprise SP, and to perform an action on an object a user must have both categories of the permission to perform that action. grant or deny a user the potential to perform actions on types of objects. grant or deny a user the potential to perform actions on a particular object or on all objects within a particular folder.
A user can perform an action on an object only if that user has role-based permission to perform the action on that type of object and has object access permission to perform the action on that particular object or on all objects in the folder containing the object. An exception is List permission for Folders, which cannot be explicitly granted as a role-based permission.
Tip: If you have a small organization and do not want to limit access for any users, you can assign all users the role and grant all object access permissions for all types of objects to the root folder.
 Permissions can be inherited
Permissions can be inherited
Although permissions can sometimes be granted or denied directly, often they are inherited. A user may inherit the role-based permissions and object access permissions of any group in which that user has membership. Objects may inherit the permissions of the folder in which they are contained, and each folder may inherit permissions from the folder in which it is contained.
Note: Any object access permission for the root folder in Loftware Enterprise SP that is configured as Inherited (a clear check box  ) is denied.
) is denied.
Additionally, a device inherits object access permissions and role-based permissions from the device group that is its parent. It is recommended that you configure permissions at the level of a device group rather than at the level of a device.
The object access permissions that a user receives for a specific object can be directly assigned to that user, inherited from a group in which the user has membership, inherited from the Default Permissions for the object, or inherited from a folder.
The role-based permissions that a user receives for a type of object can be inherited from a group to which the role was assigned or inherited from a role. These permissions cannot be directly assigned to a user.
 Order of evaluation limits inheritance
Order of evaluation limits inheritance
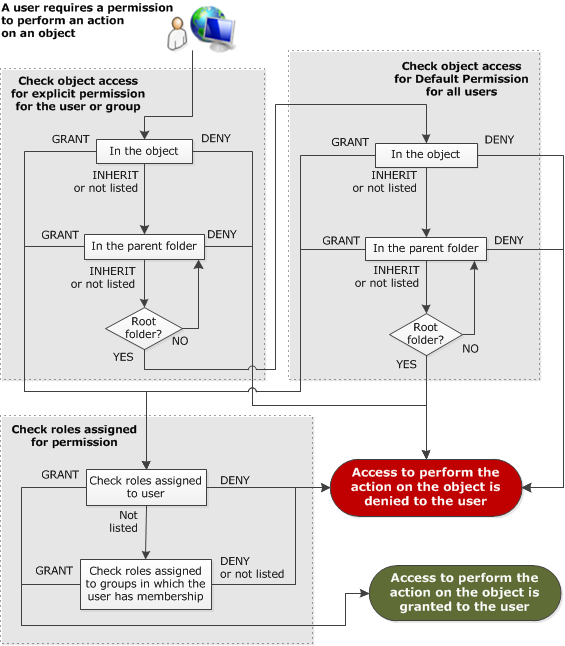
When a user attempts to perform an action on an object, Loftware Enterprise SP evaluates the permissions available for that user in order. Loftware Enterprise SP begins by evaluating any object access permissions explicitly configured for the user or any group in which the user has membership. If no explicit value is found for the permission, Loftware Enterprise SP also evaluates the Default Permissions available for all users. If object access permission is granted, then Loftware Enterprise SP evaluates the role-based permission available to the user. If role-based permission for the action is also granted, then the user can perform the action.
The following flowchart describes the order in which Loftware Enterprise SP searches for a permission and the circumstances under which it stops searching for permission.
 Object access permissions should be configured at the folder level
Object access permissions should be configured at the folder level
Object access permissions assigned to a folder are inherited by all objects of the appropriate type within that folder. For ease of maintenance, it is recommended that you assign permissions to folders instead of assigning permissions to individual objects within folders. Also, some object access permissions, such as those for Jobs and User Profiles, can only be configured at the folder level.
Tip: To view the contents of a folder, including its subfolders, you must have List permission granted for the folder. If List permission is denied for a parent folder, then you cannot view the contents of that folder, including any of its subfolders.
 All users must be assigned a role
All users must be assigned a role
Roles are used to define functions or business responsibilities. For example, you may have a role for any user acting as a and another role for a user acting as a . By using a role, you can assign a re-usable and centrally-configurable collection of permissions to users and groups.
A user must have a role to be able to perform actions in Loftware Enterprise SP. Although it is possible to assign a role directly to a user, it is recommended that you assign roles to groups and then assign users to each group (or assign groups to each user). Each user inherits the role-based permissions of any group in which the user is a member.
Tip: If you have a small organization and do not want to limit access for any users, you can assign all users the role and grant all object access permissions for all types of objects to the root folder.
 Visual indication of complex inheritance is limited
Visual indication of complex inheritance is limited
For a group, the displays each role assigned to the group and the displays users who are members of that group and therefore inherit those roles. However, for a user the displays the group in which the user has membership, but the Roles dialog box does not display roles that are assigned to the user due to group membership. The Roles dialog box for the user displays only roles that are directly assigned to the user, not those that are inherited.
When you create a folder within a folder and configure an object access permission of the child folder as inherited, the child folder inherits that permission from the parent folder. However, the Default Permissions panel of the child folder indicates only that the permission is Inherited  , not what the inherited value of the permission is.
, not what the inherited value of the permission is.
Note: Any object access permission for the root folder in Loftware Enterprise SP that is configured as Inherited  is denied.
is denied.
Note: For some special roles and user accounts, such as the ROLE_ADMINISTRATOR role and the SuperAdmin, ClientAdmin, and SystemAdmin users, some granted permissions may not be displayed.
Best Practices for Access Control
- Create folders for objects that require similar permissions, and then assign object access permissions at the folder level by using Default Permissions.
- Configure role-based permissions for roles, assign roles to groups, and add users to groups.
- Limit the number of roles assigned to a user to prevent conflicting permissions. Ideally each user should have only one role.
Important! After installing Loftware Enterprise SP and before you create any objects, you should rename the root folder (initially named Default) to something relevant to your organization. In a , the name of the root folder must be the same at the headquarters (HQ) and at each facility associated with that HQ.
 Controlling Access in Loftware Enterprise SP
Controlling Access in Loftware Enterprise SP The ability to maintain distinct versions of a label template or other object. An object is checked out to be modified, and checked in to save a new version. After a version is checked in, that version cannot be changed. for objects in that folder.
The ability to maintain distinct versions of a label template or other object. An object is checked out to be modified, and checked in to save a new version. After a version is checked in, that version cannot be changed. for objects in that folder.![]() A permission can be granted or denied
A permission can be granted or denied
![]() Permissions are specific to object type
Permissions are specific to object type
![]() Both object access permission and role-based permission are required
Both object access permission and role-based permission are required
![]() Order of evaluation limits inheritance
Order of evaluation limits inheritance
![]() Object access permissions should be configured at the folder level
Object access permissions should be configured at the folder level
![]() All users must be assigned a role
All users must be assigned a role
![]() Visual indication of complex inheritance is limited
Visual indication of complex inheritance is limited
![]() A configuration of a Loftware environment that includes Loftware instances located at different sites within the same WAN. In a multi-site deployment, each Loftware instance acts as either a headquarters or a facility., the name of the root folder must be the same at the headquarters (HQ) and at each facility associated with that HQ.
A configuration of a Loftware environment that includes Loftware instances located at different sites within the same WAN. In a multi-site deployment, each Loftware instance acts as either a headquarters or a facility., the name of the root folder must be the same at the headquarters (HQ) and at each facility associated with that HQ. ) is denied.
) is denied.