Cloud Database
Your
Example
When you are designing food labels with automatically highlighted allergens on the ingredients list, you can store the allergens' data in your Cloud database. At print time, your Loftware client (Desktop Designer, Print, or Web Client) retrieves the data from the Cloud Database, and prints the labels with highlighted ingredients that are marked as allergens.
Note
The amount of available database space depends on your account. Please contact your Loftware sales representative for more details.
Setup your
Go to
Administration >Storage >Cloud Database for Your Content .Click the
Create labeling database button. TheNew labeling database window opens.Type in your user name and set the password. You will need these credentials later when connecting to the Cloud database from your labels, solutions, or configurations. The credentials are also mandatory if you want to connect to the database using your database editing software.
Note
You can connect to the Cloud database using any compatible SQL tool. Loftware recommends Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio.
The SQL user name you create is assigned administrator permissions in your SQL database. You can define additional SQL users in Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio. For example, you can limit SQL users to specific tables in your (one) SQL database, or for security, define a "working user" that is not an administrator.
Click
Create . When the window closes, your database is ready. You seeCloud Database information underCloud database for your content :Status displays yourCloud Database creation date.Connection string example displays the connection string format for yourCloud Database in the cloud. To connect your Loftware clients to this database, update the connection string with your Loftware Cloud account user name and password.
Connect to your Cloud database:
Note
You can connect to your Cloud Database using any compatible SQL tool. Loftware recommends Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio.
In Control Center go to
Administration >Storage >Cloud Database for Your Content .Copy the
Server name from theConnection string example .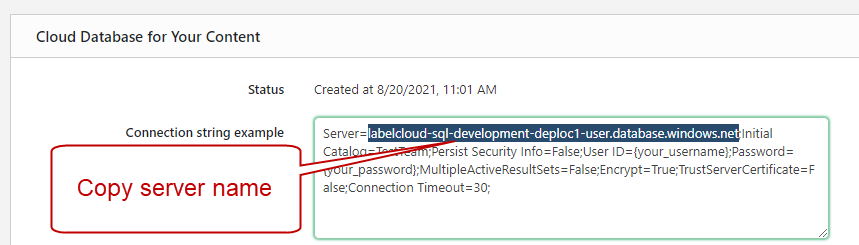
Open Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio.
The
Connect to Server window opens. Paste theServer name from theConnection string example .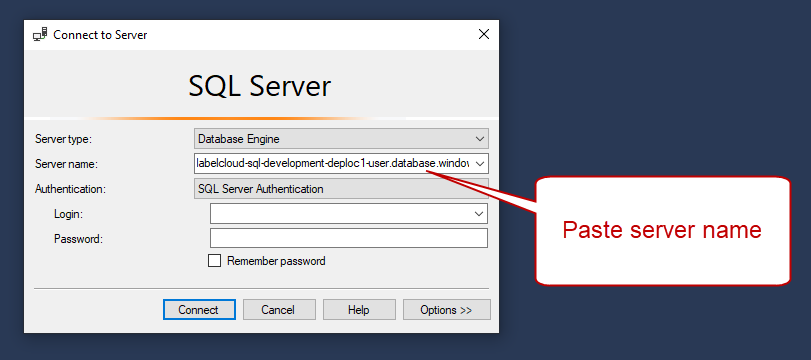
Set
Authentication toSQL Server Authentication .Type in your database credentials.
Click
Options and go toConnection Properties tab. Copy the database name from theConnection string example to theConnect to database field .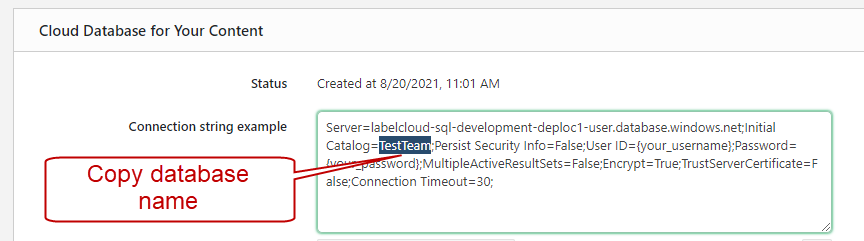
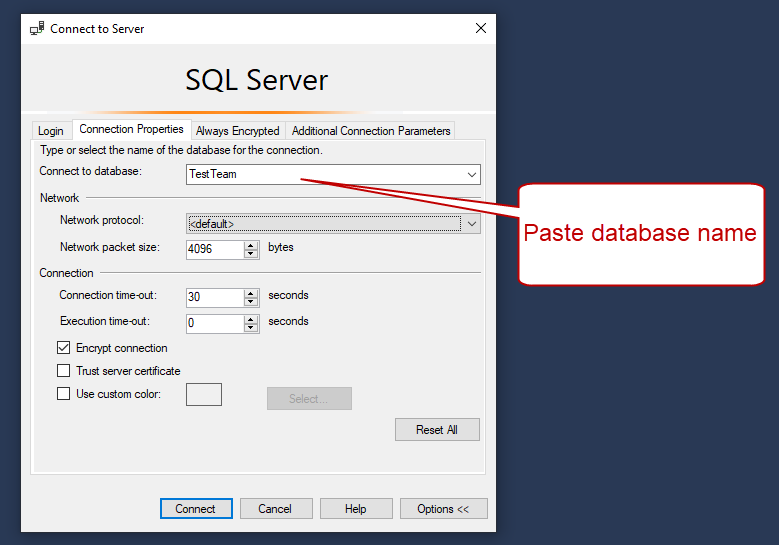
Click
Connect .
Your
Cloud Database User Permissions
Loftware Control Center allows different users to access Cloud Database with different levels of permissions.
The SQL user name you create is assigned administrator permissions in your SQL database. You can define additional SQL users in Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio (or similar SQL management tools). For example, you can limit SQL users to specific tables in your SQL database, or for security, define users that are not administrators.
Since the database instance does not allow adding logins directly, add database users and roles using Transact-SQL (T-SQL) commands.
Below are the options for different user roles and their respective permissions:
Administrators have full access to the database. They can create, modify, and delete database structures and manage all user permissions. The initial login created from the cloud setup is assigned administrator permissions.
Label designers have permissions to select, insert, delete, and update data. This role is ideal for users who need to design and manage labels, requiring more access than a printer operator but less than an administrator.
Example
T-SQL command to create a user with select, insert, delete, and update permissions:
CREATE USER [DATA_MANAGER] WITH PASSWORD = '';EXEC sp_addrolemember N'db_datareader', N'DATA_MANAGER';EXEC sp_addrolemember N'db_datawriter', N'DATA_MANAGER';Printer operators have read-only access to the database. They can view data but cannot make any modifications. This role is suitable for users who need to print labels without altering the database content.
Example
T-SQL command to create a read-only user:
CREATE USER [OPERATOR] WITH PASSWORD = '';EXEC sp_addrolemember N'db_datareader', N'OPERATOR';
Note
See also the Access Roles topic on how to assign different roles and permissions to different users.
Cloud Database Password Complexity
Cloud Database uses Microsoft SQL Server password policy.
But there is one exception. When applyinng the rule "The password doesn't contain the account name of the user", the underscore sign (_) in the account name causes an isue where you can't use parts of the account name before and after the underscore sign in your password.
For example, If your account name is "John_Doe", your password must not contain the following strings:
John_Doe
John
Doe